Surgical instruments
Recent infection control lapses due to non-compliance with recommended reprocessing procedures highlight a critical gap in patient safety.” CDC Feb2022

If it’s not clean, it shouldn’t be sterilized
It is impossible to disinfect or even sterilize an inadequately cleaned instrument.⁴
Any disinfection process is doomed to fail if cleaning is inadequate.⁴
4. CSS, BE: Recommandationsd’entretien du matérielendoscopique et de prévention des infections –2010
Bioburden
on surgical instruments
Bioburden refers to the population of viable micro-organisms contaminating an object, although it is also often used to describe residual organic material (protein etc.) on surgical instruments.⁵
Inorganic and organic materials interfere with the efectiveness (i.e. antimicrobial activity) of disinfectants and sterilization.²
2. CDC guidelines
5. ANSI/AAMI ST79:2010, Patient Safety Advisory, Pennsylvania PSRS
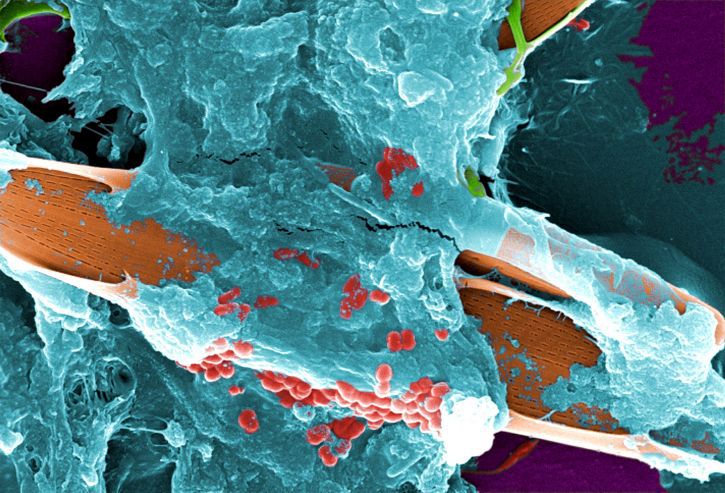
Bioburden & biofilms in brief
Biofilm is an aggravating factor in bioburden removal strategies as 99% of bacteria exist in the form of a biofilm.⁶
Biofilms form a protective barrier around infectious micro-organisms and often form on medical devices.
Biofilms and bioburden, including protein soiling, must be eliminated to ensure disinfection and sterilization.
Biofilms enhance survival of exposure to antimicrobials due to structural and functional properties of biofilm matrix.
Bacteria are up to 1000x more tolerant to biocides when in a biofilm. ⁷
AN ITEM THAT HAS NOT BEEN CLEANED CANNOT BE ASSUREDLY DISINFECTED OR STERILIZED. Public Health Agency of Canada
6. Berk et al. 2012
7. BO Santé – Protection sociale – 2012
Other applications

endoscopy
10 to 30% of patient-ready endoscopes are contaminated with microorganisms.

surgical instruments
Over 60% of correctly-processed surgical instruments exhibit residual protein soiling.

surfaces
Working in a safer & cleaner environment is a must. Take control.